Introduction
Domain Name System (DNS) is a crucial service in networking that translates human-readable domain names (like https://optimusing.dyndns.org) into IP addresses. Proper DNS configuration on network devices is essential reliable name resolution, ensuring users can access web and other services. In this article, we’ll guide you through configuring DNS on a FortiGate firewall.
More information about FortiGate DNS configuration you can found on the link .
Steps to Configure DNS Server on FortiGate Interface
Step 1: Access the FortiGate Web Interface
- Open a web browser and enter the IP address of your FortiGate device.
- Login using your admin credentials.
Step 2: Navigate to DNS Settings
Once logged in, go to:
- Network > DNS.
- You will see options for both System DNS and DNS servers.
Step 3: Configure System DNS
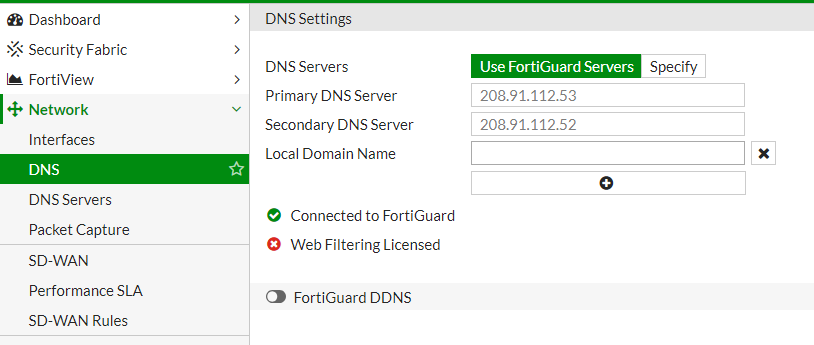
The System DNS servers are used by FortiGate itself to resolve domain names for its services (e.g., checking updates, remote logging). To configure:
- Under Network > DNS:
- Select System DNS.
- Enter the primary and secondary DNS servers. Common choices include Google’s DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare’s DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1) or use FortiGuard Servers.
- Click Apply to save the settings.
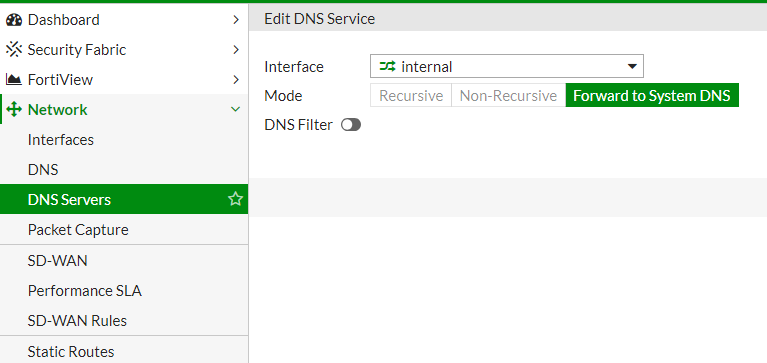
Step 4: Configure DNS Forwarding
FortiGate can also act as a DNS forwarder, meaning it can resolve DNS queries for devices on the network. This offloads DNS lookups to a trusted source and reduces DNS-related traffic.
To configure DNS forwarding:
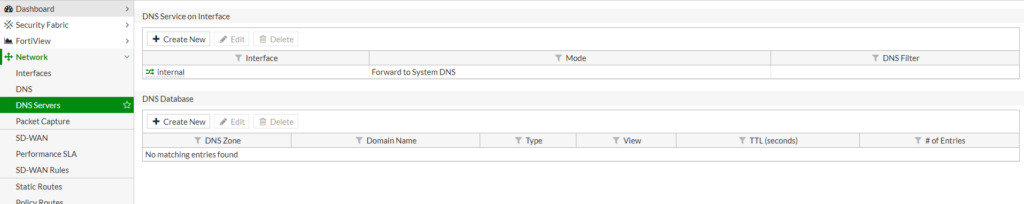
- Go to Network > DNS Servers.
- In the section DNS Service on Interface create a new DNS service on your internal network interface.
- If you need to resolve something from local netowork add it in the section DNS Database
- Once configured, click Apply.

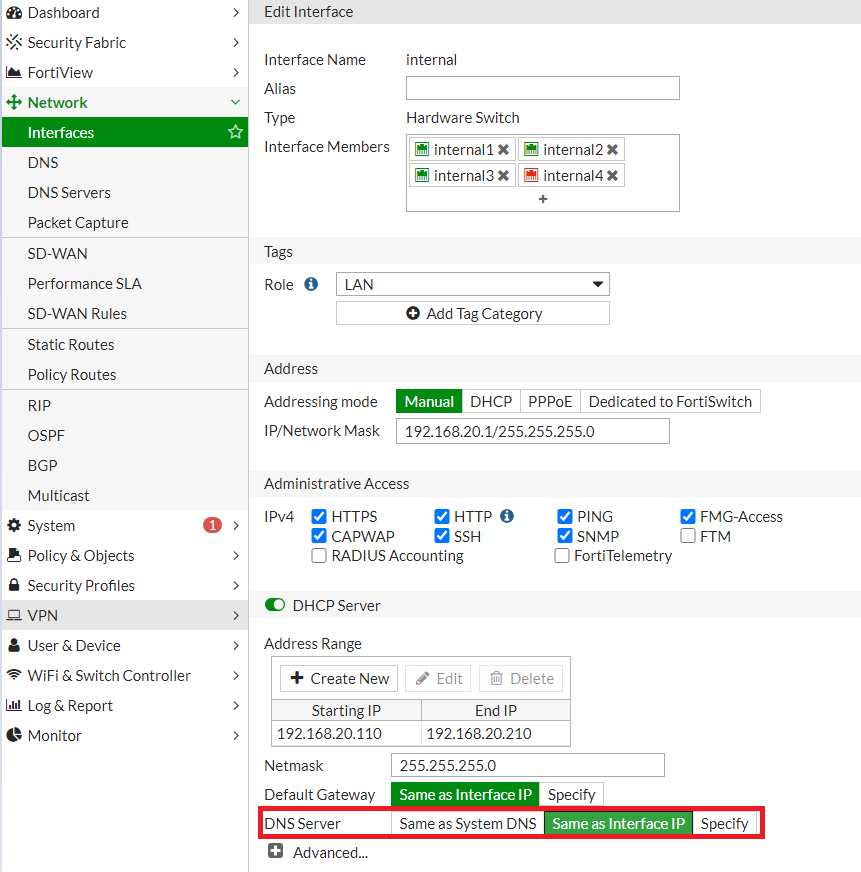
Step 5: Enable DNS on Local interface
- Go to Network > Interface
- Select Internal interface.
- In section DNS Server select Same as Interface IP to use FortiGate DNS Server in your local network.