Introduction
Understanding how traffic routes (routing monitor) through a network is crucial for network management, especially when dealing with multiple networks (for example internal networks) and gateways (Interenet Service Provicdes). FortiGate’s Routing Monitor and Route Attributes provide insights and controls to fine-tune your network’s behaviour. This article will guide you through FortiGate’s Routing Monitor interface, show you how to interpret key route attributes, and explain how to use this information to optimize network performance.
What is FortiGate Routing Monitor?
For all sessions, FortiGate is performing a routing table lookup twice:
- For the first packet sent from sender
- For the first replay packet coming from responder
Routing information are written in to the session table.
More information about routing you can find on the link. For the FortiGate Static Routes, you can check the article.
Routing Protocols on FortiGate Device
FortiGate support the following Dynamic Routes protocols:
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) → is not listed on my firmware (v6.0.13)
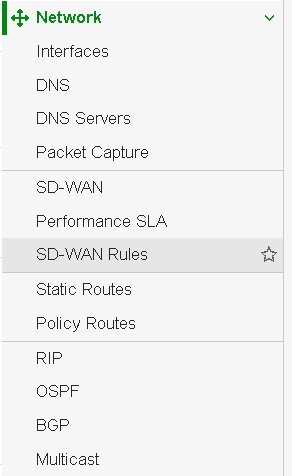
If you are not able to see these protocols on your device, you can enable them. How to enable these protocols (hidden features), you can check at the following link.
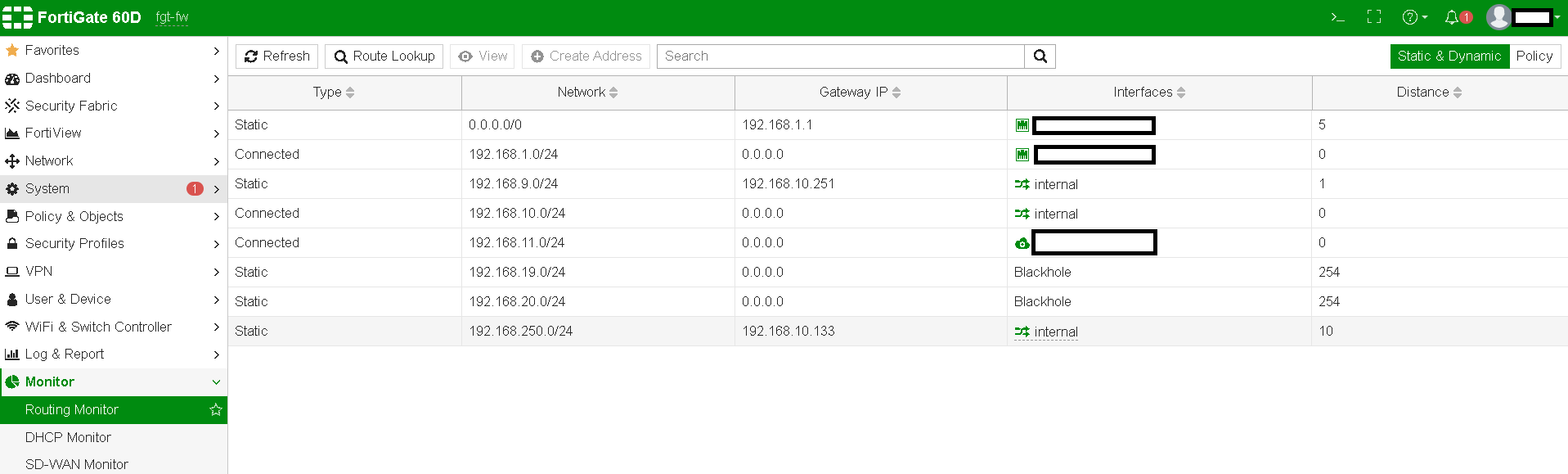
FortiGate Routing Monitor
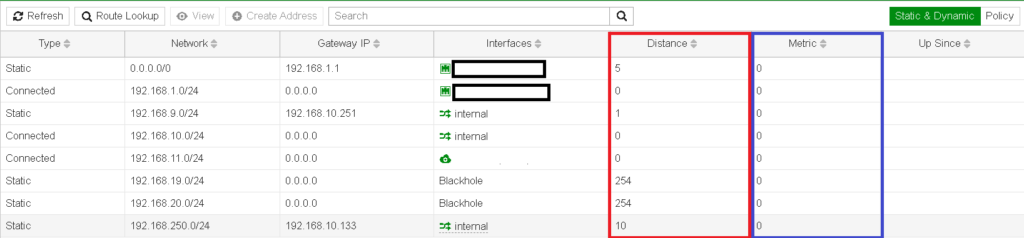
The Routing Monitor on FortiGate offers a real-time view of your routing table, showing the active routes for your traffic. It’s a tool that provides visibility into how the firewall is forwarding packets based on IP destinations, allowing administrators to check which routes are prioritized and troubleshoot any routing issues.
- How to Access: The Routing Monitor is accessible via the FortiGate GUI by navigating to
Monitor->Routing Monitor. - Key Interface Details: It displays details like destination IP, gateway, interface, and metric, which can all help in analysing routing decisions.
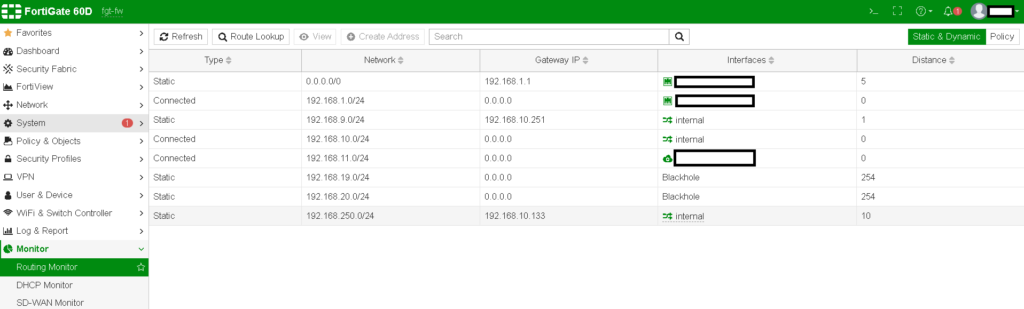
Understanding Route Attributes
Route attributes are essential for determining the path selection for traffic within FortiGate. Attributes such as administrative distance, priority, and metric are displayed in the Routing Monitor and influence which routes are used and which are kept as backups.
- Administrative Distance (AD): The AD represents the trust level for different routing protocols. A lower AD value is more trusted and thus preferred.
- Priority: Routes can be assigned priority values to specify which route should be used when multiple routes are available.
- Metric: This value typically represents the ‘cost’ of a route, with lower metrics being preferred.
In my case, all routing attributes are not shown because of old firmware.
Key Scenarios: How Route Attributes Affect Traffic Flow
Different route attributes play a role in how traffic is routed, especially in complex networks with multiple gateways or VPN connections. Here are a few scenarios:
- Load Balancing and Redundancy: FortiGate can route traffic based on priority and metrics for load balancing or backup paths.
- Failover Situations: When a primary route fails, routes with higher AD or lower priority are used, ensuring consistent connectivity.
- Policy-Based Routing (PBR): By combining PBR with route attributes, specific traffic can be directed through preferred gateways, optimizing latency-sensitive applications. If you have a two internet links (A and B) you can route packets from low-priority source IPs on A and packets from high-priority sources on B link.
- More granular matching than static routes based on protocol, source address, source ports, type of service (ToS) bits and destination ports.
- Policy-Based Routing (PBR) have precedence over the routing table (maintained in a separate routing table)
- Internet Services Routing
- Route well-known Internet services through specific WAN Interface
The Distance, Metric and Priority are attributes used by FortiGate to make route selection decisions.
Route Attribute: Distance
If the multiple routes for the same destination exist, the one with the lowest distance will be active. To check it open Monitor → Routing Monitor
The following shows the default distance (preference) settings on a FortiGate (configurable for all types except direct interfaces) :
| Route | Distance |
|---|---|
| Directly connected | 0 |
| DHCP Gateway | 5 |
| Static routes | 10 |
| External BGP (EBGP) routes | 20 |
| OSPF routes | 110 |
| RIP routes | 120 |
| Internal BGP (IBGP) routes | 200 |
Route Attribute: Metric
If the multiple dynamic routes have the same distance, then the metric is used for selection process. The route with the lowest metric is chosen.

The calculation method differs for different routing protocols.
Route Attribute: Priority
If the multiple static routes have the same distance, they are all active, only the one with the lowest priority is considered the best path.
Configuring and Troubleshooting Route Attributes in FortiGate
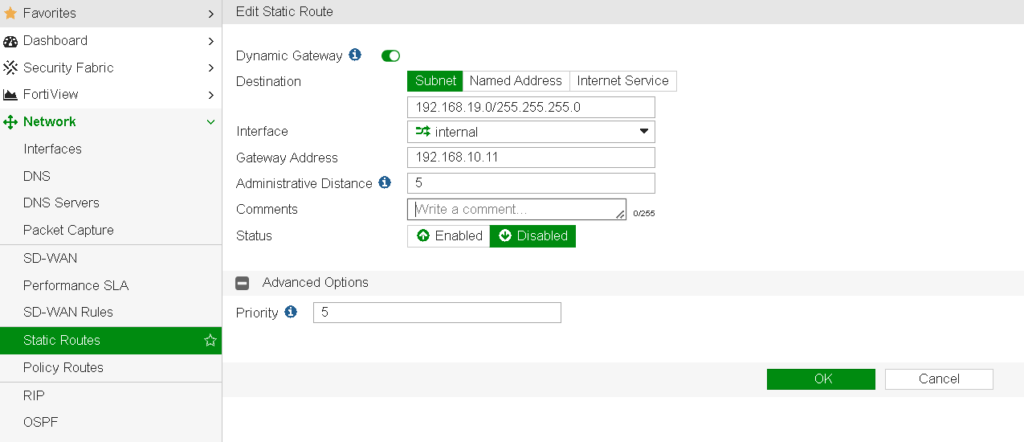
You can configure these attributes within the Network -> Static Routes section or by using CLI commands to gain finer control. Troubleshooting involves checking the Routing Monitor to see if routes are active and evaluating why certain routes are preferred over others.
- Using CLI for Custom Configurations: Commands like
get router info routing-table allprovide detailed routing tables and can help diagnose routing issues. - Troubleshooting Tips: Checking administrative distance, priority, and metrics can reveal misconfigurations or unintended route selections.
fgt # get router info routing-table all
Routing table for VRF=0
Codes: K - kernel, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, B - BGP
O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [5/0] via xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, wan1
C /30 is directly connected, wan1
S 192.168.10.0/24 [4/0] is directly connected, to1
S 192.168.11.0/24 [10/0] is directly connected, to1
S 192.168.19.0/24 [10/0] via 192.168.20.112, internal
C 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, internal
Conclusion
The Routing Monitor and route attributes on FortiGate are essential tools for network administrators aiming to streamline traffic flow and ensure network resilience. By understanding and adjusting route attributes, you can optimize traffic handling, reduce latency, and maintain control over your network’s behaviour.