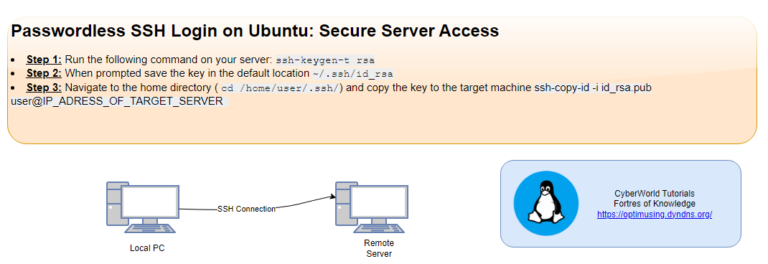
Network Security Topics
What is Port Forwarding?
Port forwarding, also known as port mapping, is a technique used to redirect communication requests from one address and port number combination to another while packets traverse a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. It is commonly used to allow remote computers to access specific applications hosted on a private network.
Port forwarding is a crucial feature in network security, allowing external devices to access services on a private network through a firewall. Fortinet’s FortiGate firewall provides robust port forwarding capabilities that are essential for businesses to manage traffic effectively and securely. This guide will walk you through the steps to configure port forwarding on a FortiGate firewall.
Why Use Port Forwarding on FortiGate?
- Remote Access: Enable remote users to connect to services such as web servers, FTP servers, or other applications on the internal network.
- Security: FortiGate offers advanced security features that help protect internal services from unauthorized access while allowing legitimate traffic.
- Network Optimization: Efficiently manage and optimize traffic flow between the internet and internal network resources.
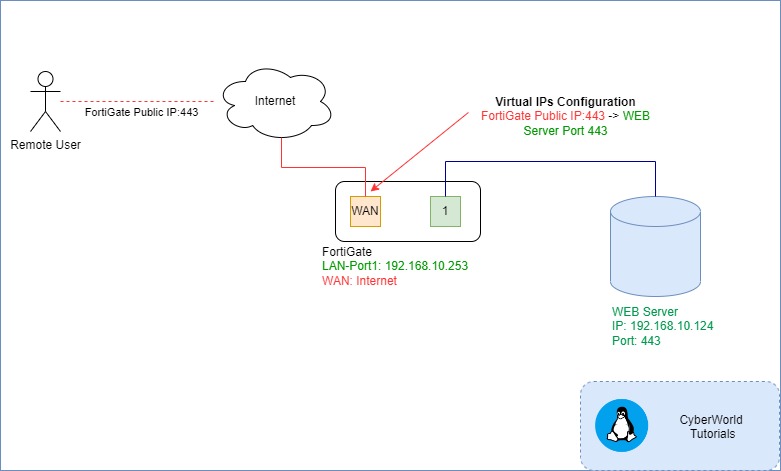
Details:
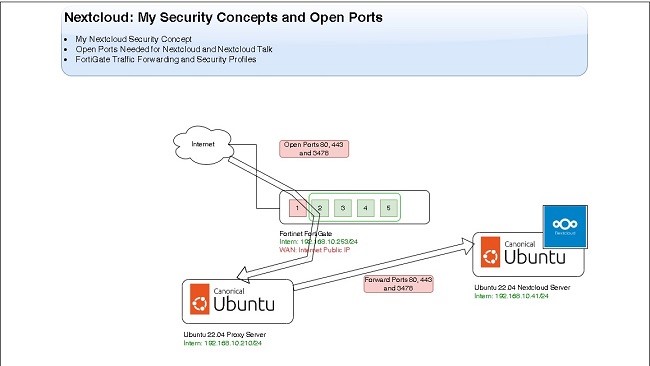
- FortiGate WAN: DHCP
- FortiGate Intern IP: 192.168.10.253
- WEB Server IP: 192.168.10.124 -> Port 443 (Web Server)
Prerequisites
Before configuring port forwarding on your FortiGate firewall, ensure that:
- You have administrative access to the FortiGate management interface.
- You know the internal IP address and port number of the device or service you want to forward traffic to.
- You have the external IP address (usually the WAN IP) where the traffic will be forwarded.
Configuring Port Forwarding on FortiGate
Step 1: Access to the Fortinet FortiGate Device
- Open a web browser and enter the FortiGate management IP address.
- Log in using your administrative credentials.
Step 2: Create a Virtual IP (VIP)
- Navigate to Policy & Objects > Virtual IPs.
- Click Create New and select Virtual IP.
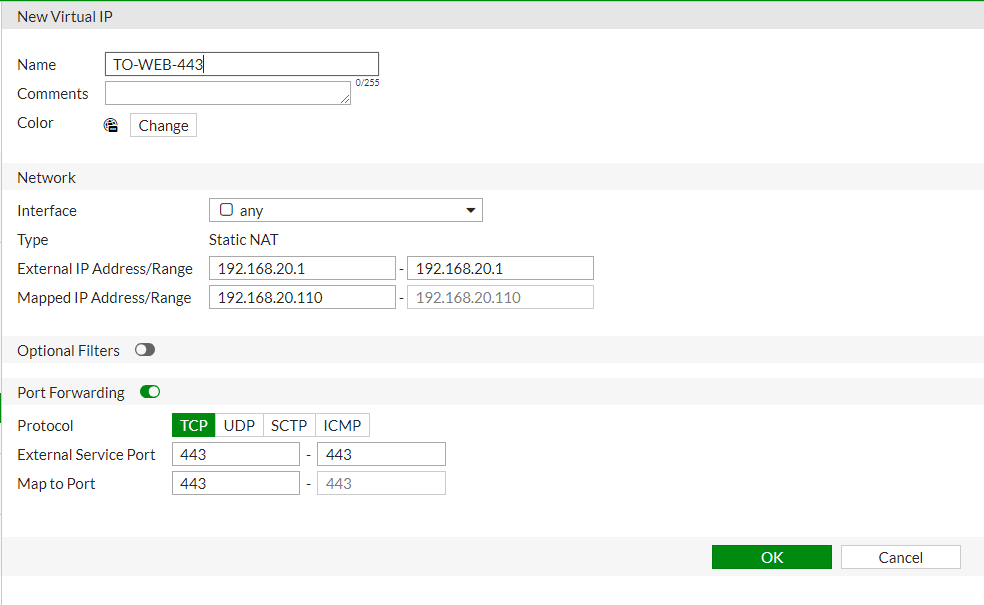
Configure the following settings:
- Name: Enter a descriptive name for the VIP.
- Interface: Select the external interface (e.g.,
wan1). - External IP Address/Range: Enter the public IP address or range that will be used for the port forwarding.
- Mapped IP Address/Range: Enter the internal IP address of the server or device.
- Port Forwarding: Enable this option.
- External Service Port: Enter the external port number (e.g.,
443forHTTPS). - Map to Port: Enter the internal port number (e.g.,
443forHTTPS).
Click OK to save the VIP.
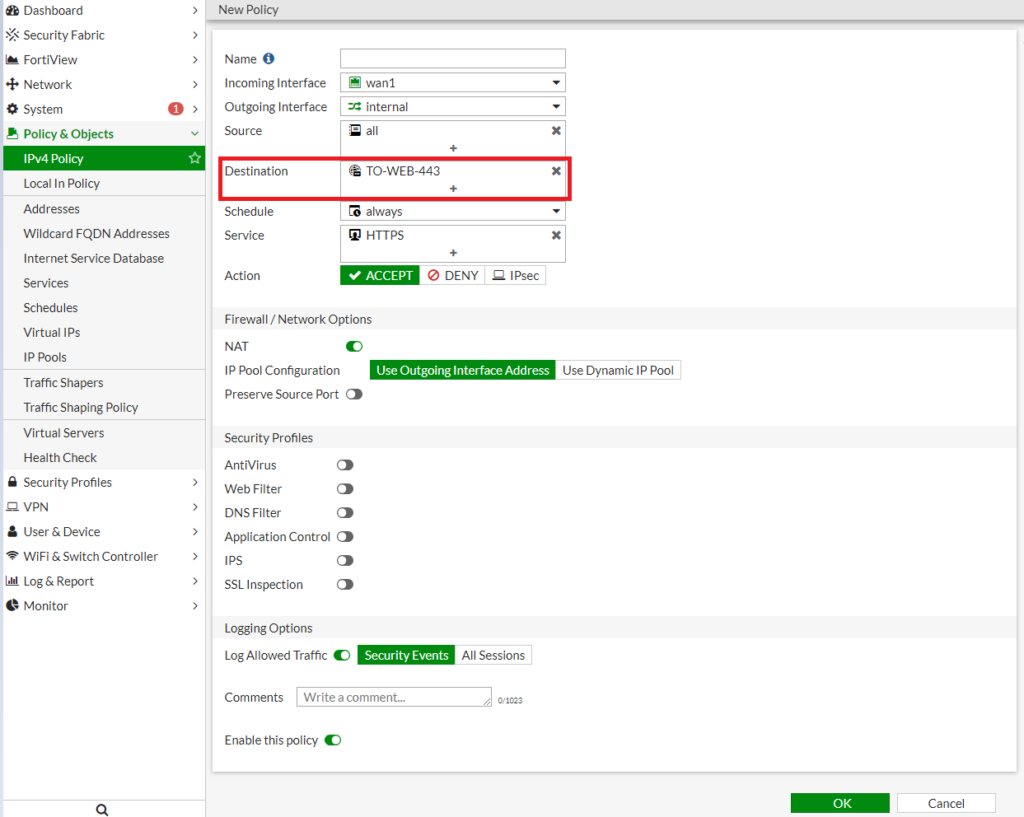
Step 3: Create a Firewall Policy
- Navigate to Policy & Objects > IPv4 Policy.
- Click Create New to add a new policy.
- Configure the following settings:
- Name: Enter a descriptive name for the policy.
- Incoming Interface: Select the external interface (e.g.,
wan1). - Outgoing Interface: Select the internal interface (e.g.,
internal). - Source: Set to All or specify specific source addresses.
- Destination: Select the VIP created in Step 2.
- Service: Choose the appropriate service (e.g.,
HTTPS). - Action: Set to Accept.
- Enable NAT if required.
- Click OK to save the policy.