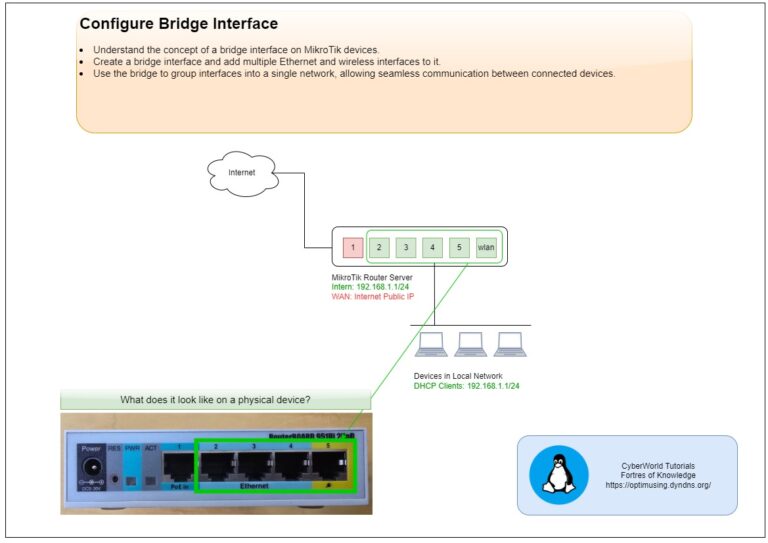
Introduction
Configuring VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) on VMware ESXi is a critical step for network segmentation, improved security, and efficient traffic management in virtualized environments. VLANs allow administrators to isolate different types of network traffic within the same physical network, which is especially useful in virtualized infrastructures where multiple VMs share the same host.
ESXi VLAN Configuration
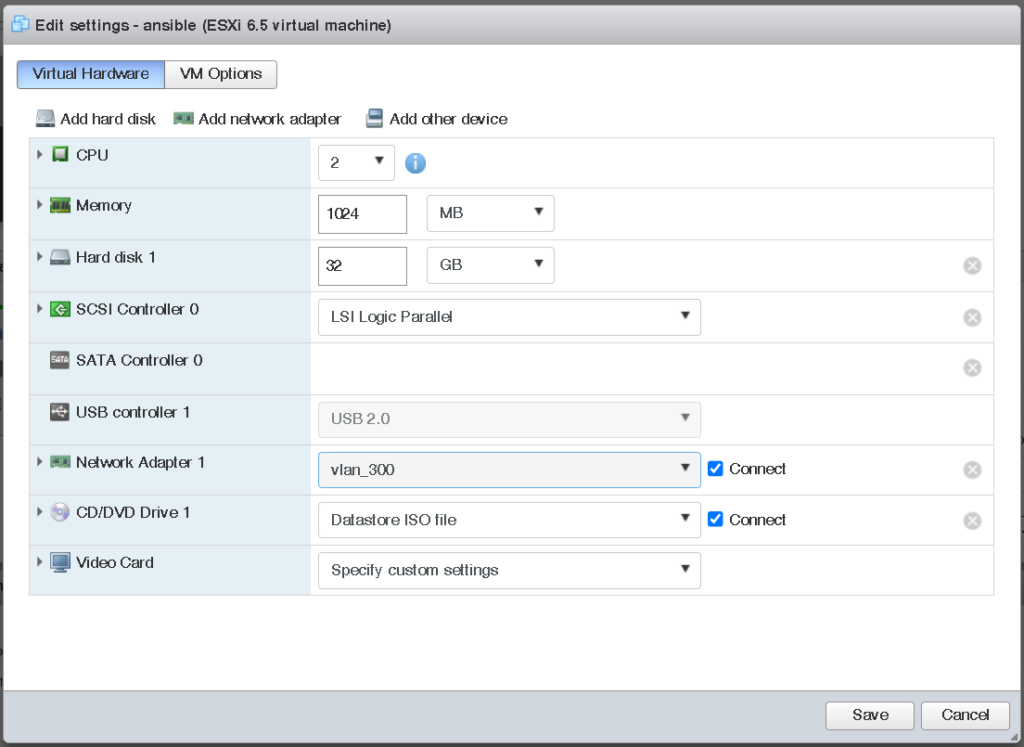
To set up VLANs on ESXi, start by accessing the ESXi Web Client or vSphere Client. Navigate to the networking section and select the virtual switch (vSwitch) you wish to configure. Each VLAN will need a unique identifier (VLAN ID), typically a number between 1 and 4094. Assign this VLAN ID to the port group associated with the virtual machines you want to segment.
In this case, we will create VLAN 300:
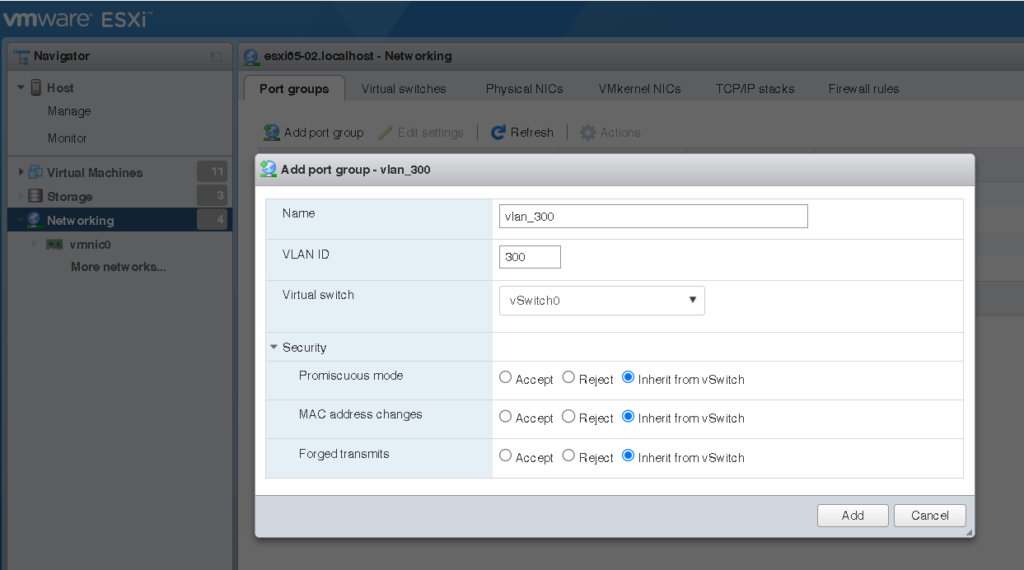
VLAN Settings:
When configuring VLANs, it’s essential to ensure that the physical switch ports connecting to the ESXi host are set to “trunk” mode to pass tagged VLAN traffic. You can also define multiple VLANs on a single vSwitch, making it easier to manage complex networks with reduced hardware.
Troubleshooting VLANs on ESXi may involve checking the vSwitch and port group settings and confirming that the physical switch is appropriately configured to pass VLAN-tagged packets. By following these steps, you can achieve efficient VLAN management, enhance security, and control traffic flow within your virtual infrastructure.
Configuring VLANs on ESXi enhances flexibility and can significantly reduce network complexity while ensuring robust isolation of sensitive traffic. Proper VLAN setup ensures optimized network performance and security across all virtual machines in the VMware ESXi environment.
Assign VLAN to Virtual Machine (VM)
- Step 1: Right click on VM
- Step 2: Click on
Edit settings
- Under
Network Adapterassign created VLAN (in my case vlan_300)